Connecting a successful phishing attempt to Scattered Spider through Validin pivoting
Even security-conscious individuals can fall victim to well-crafted social engineering attacks, especially when tired or distracted. On March 25, 2025, a sophisticated phishing attack targeted Troy Hunt, a highly regarded security researcher and the creator of Have I Been Pwned?, a free data breach search and notification service, resulting in the compromise of his Mailchimp account.
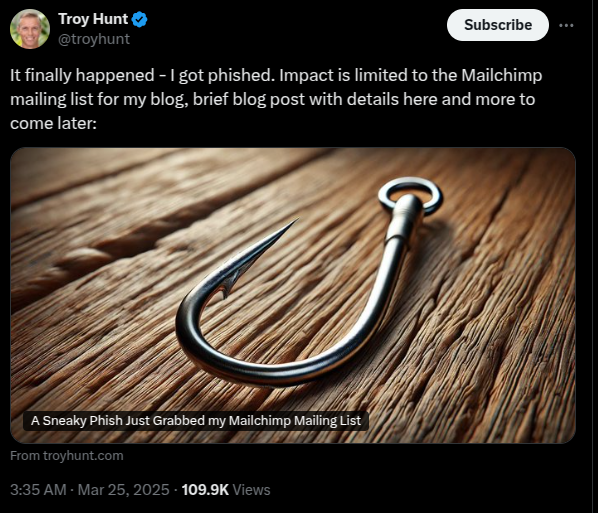
Figure. Tweet by Troy Hunt disclosing the details of the phishing attempt that targeted his mailing list.
Setting an example of openness and transparency, he immediately described the full details of how it happened, offered suggestions for how vendors with sensitive information can better protect users, and published the domain name that was created for this effort against him and possibly others: mailchimp-sso[.]com.
Using these details, I’ll show you how I used Validin’s DNS, host response, and registration data to find dozens of domain names related to the one used to phish Troy Hunt with very high confidence, ultimately linking them to the group Scattered Spider (aka 0ktapus and numerous other aliases) and over 200 related domain names.
Basic DNS Recon
We’ll begin by searching for the reported phishing domain in Validin to learn more about it.
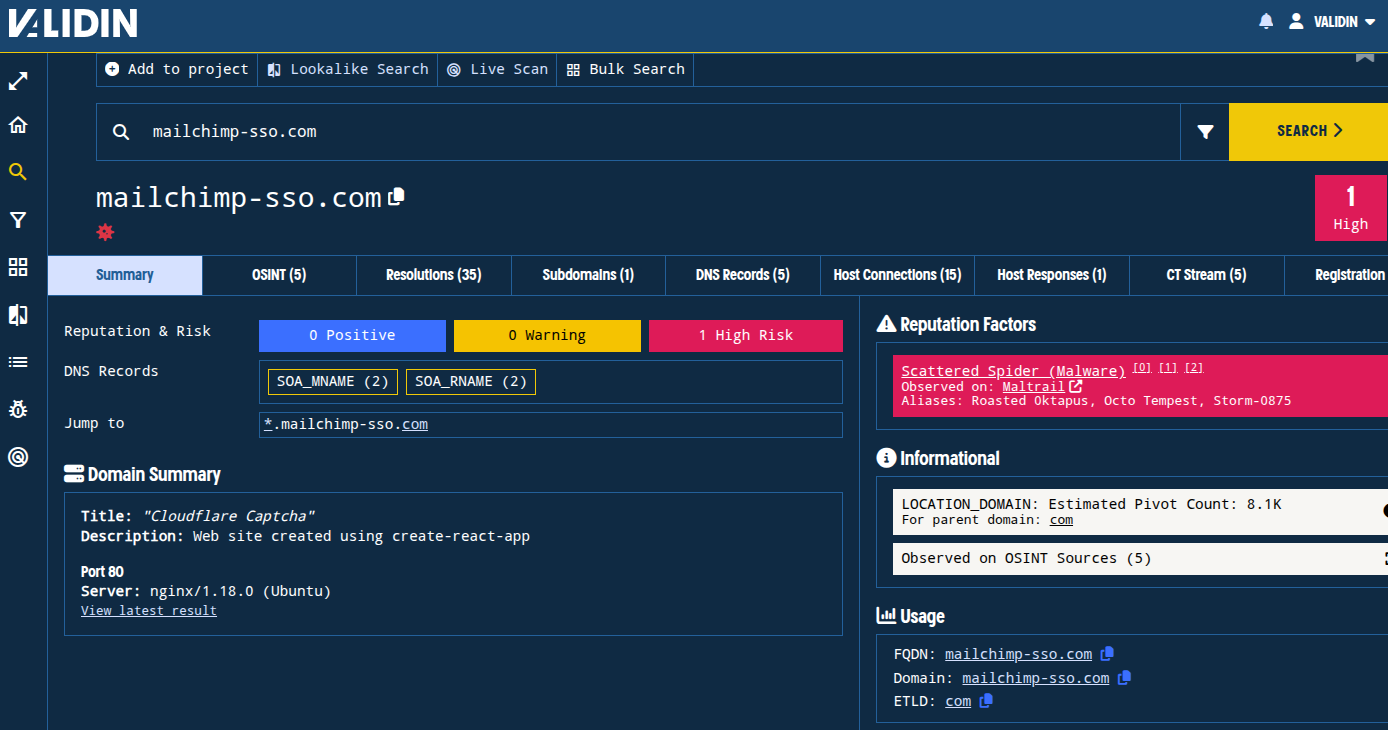
Figure. Gathering initial context about the domain used in a recent phishing attempt.
The first thing we note is that the domain is classified as “Scattered Spider.” In the citations, we note a blog from 2022 by Group-IB reporting the same domain as 0ktapus, along with a handful of others:
Figure. Indicators reported by Group-IB as related to 0ktapus from 2022.
In fact, we see that Validin has been tracking DNS history this domain since 2022 and has observed one additional period of activity in addition to the most recent:
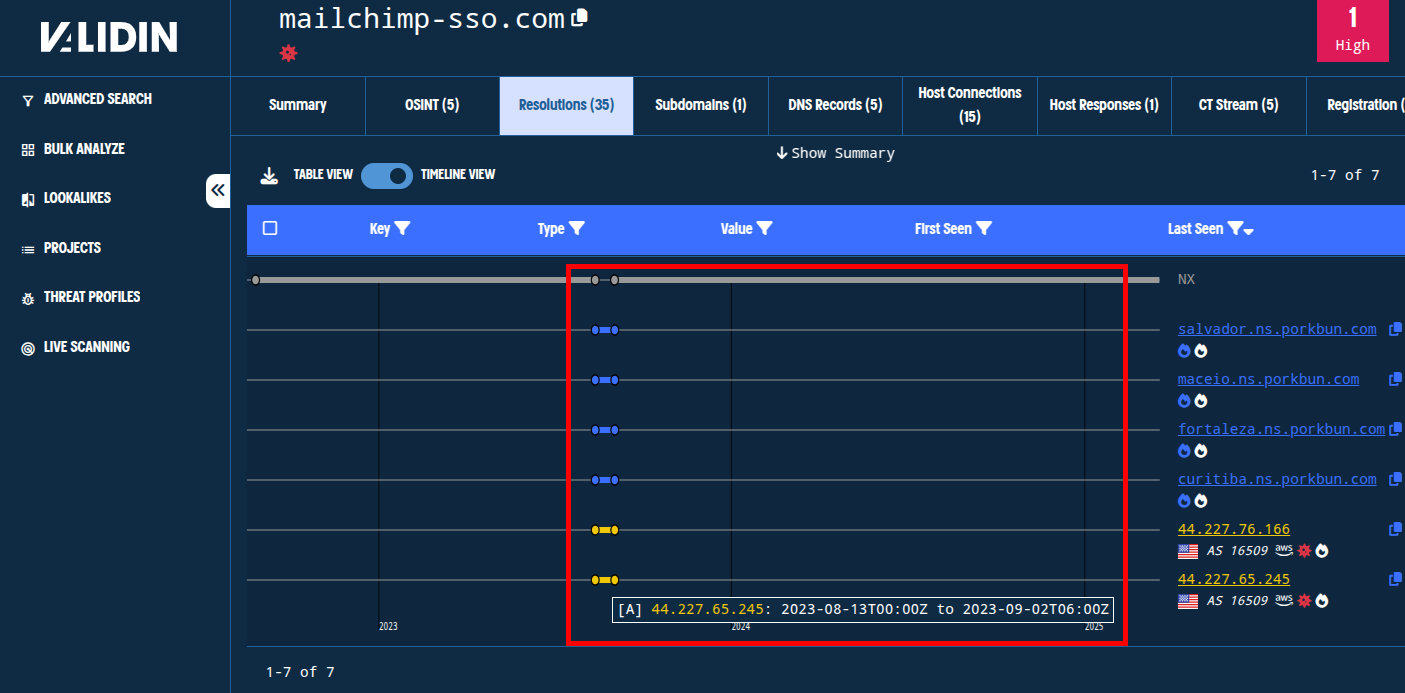
Figure. DNS resolution history shows that the domain was also briefly reactivated in 2023.
Looking at recent history, we see that the domain that phished Troy was active on Cloudflare for less than a full day, then briefly pointed to the IP 159.100.6[.]244, and now directs to a non-(publicly-)routable IP, 127.0.0[.]127. The domain also changed name servers 3 times in a 24 hour period.
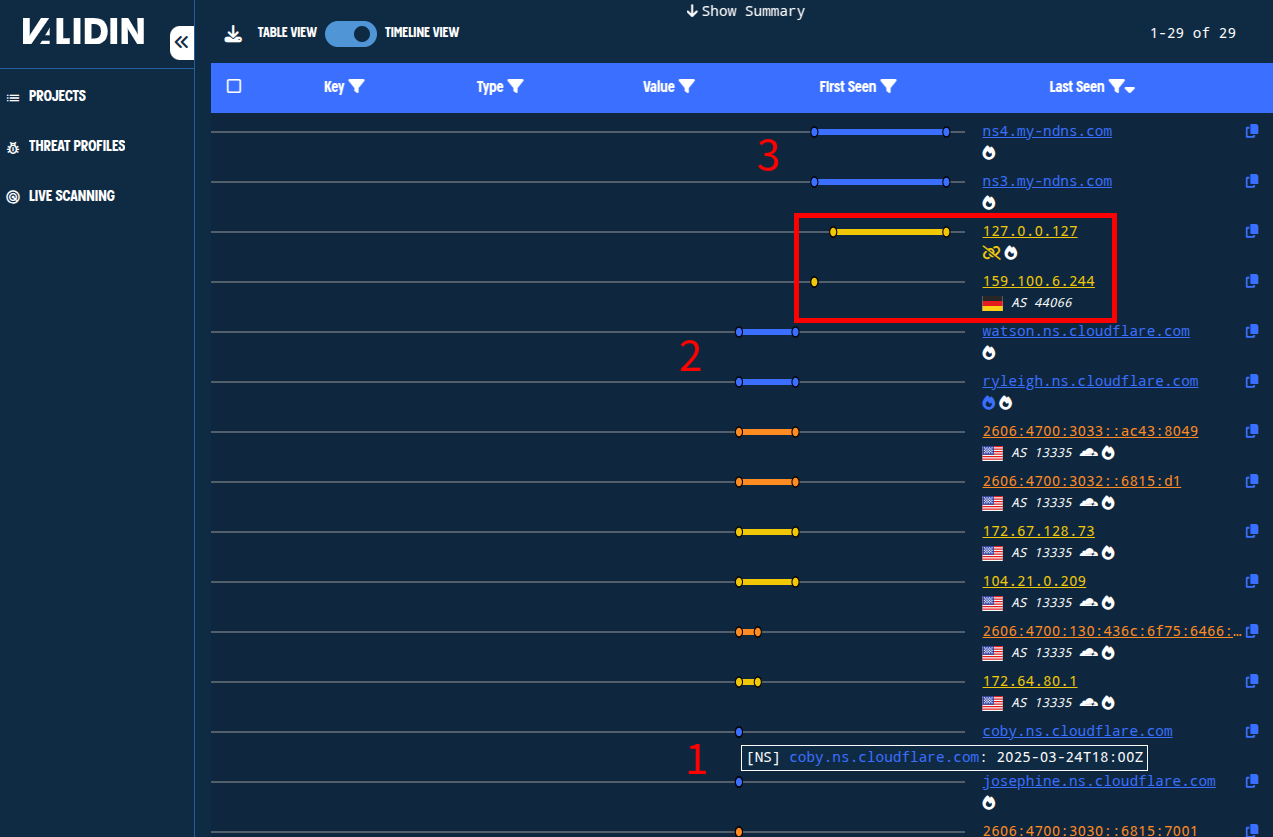
Figure. Rapid DNS changes by the known phishing domain: 3 sets of name servers, cloudflare IPs, then briefly on AS 44066, then resolving to a local IP.
We’ll note also that the domain uses self-named SOA records.
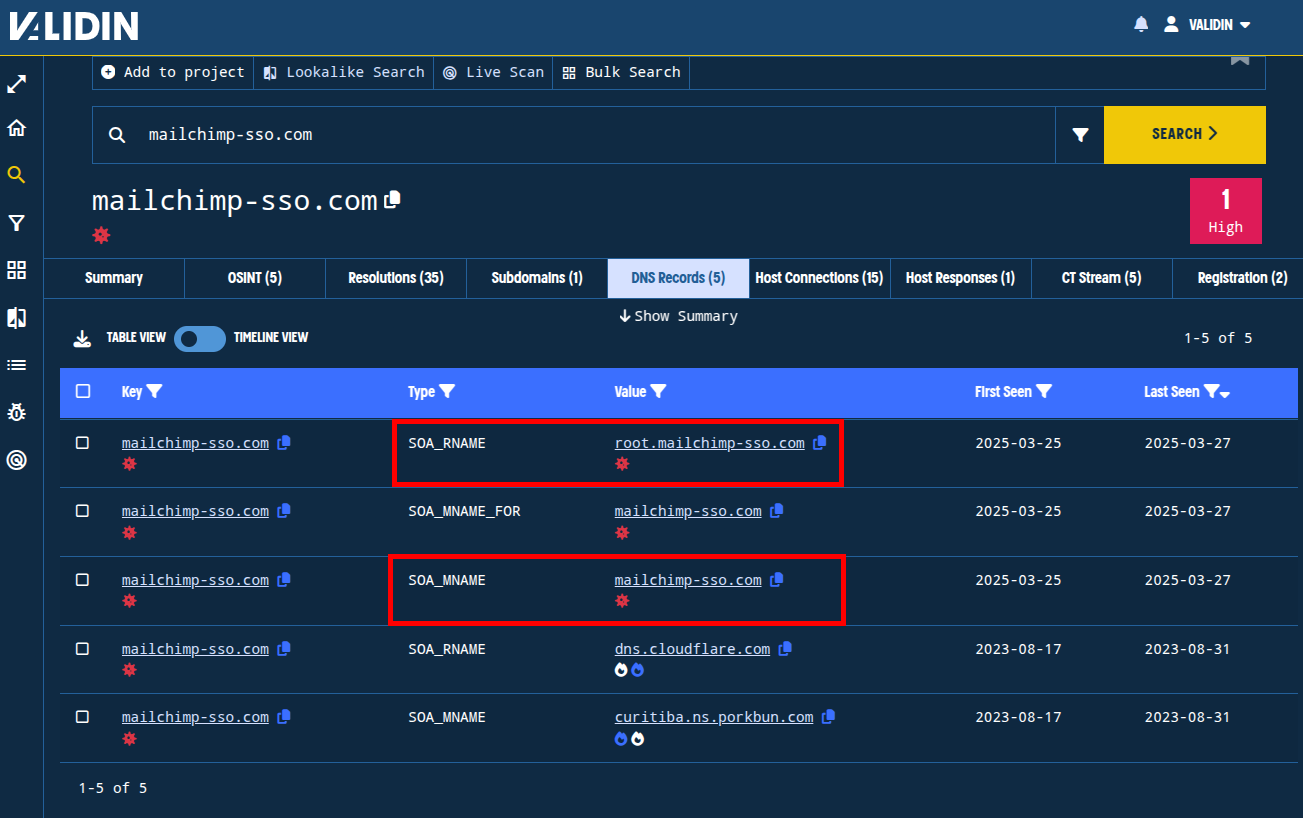
Figure. SOA contact (RNAME) and primary name server (MNAME) records are configured to itself.
Fake Cloudflare Turnstile
Validin captured a host response for this domain during the brief time that it resolved to 159.100.6[.]244. Looking at the features extracted from this host response, we observe a few rare or unique features of the response, including the favicon hash, title tag, banner hash, and body hash. Each can be potentially interesting pivots.
More interesting, though, is the use of a fake Cloudflare-style turnstile, designed to look like it is checking for human users. What makes this odd is that this isn’t hosted on Cloudflare - it’s hosted on DE-FIRSTCOLO.
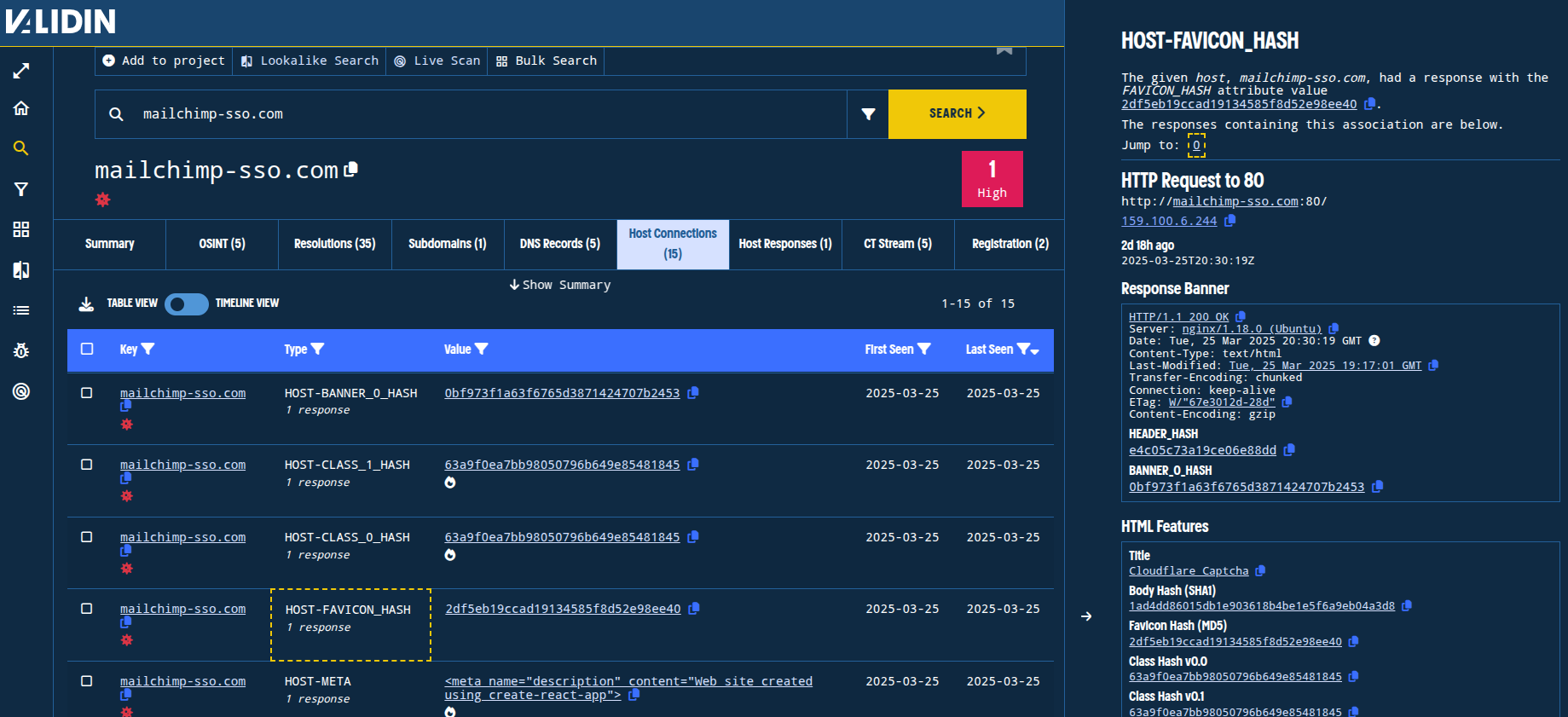
Figure. Viewing connections extracted from the host response. Connections without popularity flare are much more likely to yield tight clusters of related results.
An example of the Cloudflare-style turnstile, impersonating “Cloudflare on behalf of Mailchimp,” is shown below.
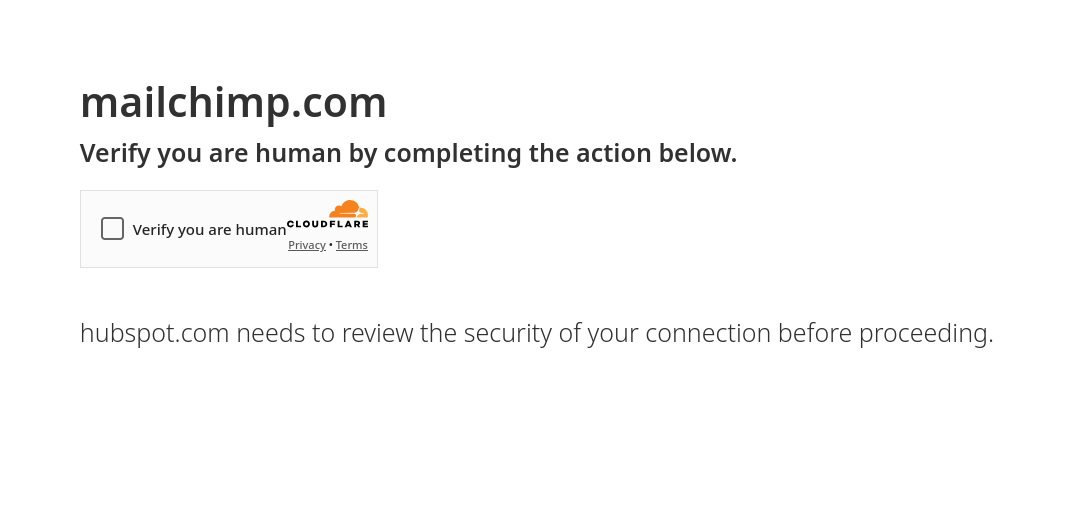
Figure. Fake Cloudflare turnstile impersonating Mailchip, as pointed out by a user on LinkedIn.
Registration Details
Finally, looking at registration history in Validin’s enterprise platform, we note a few things. First, the registrar is NICENIC INTERNATIONAL GROUP. Second, the domain was (re)registered very recently: 2025-03-24T19:23:30Z to be exact. Third, the registrant details for the “State” field appear completely bogus.
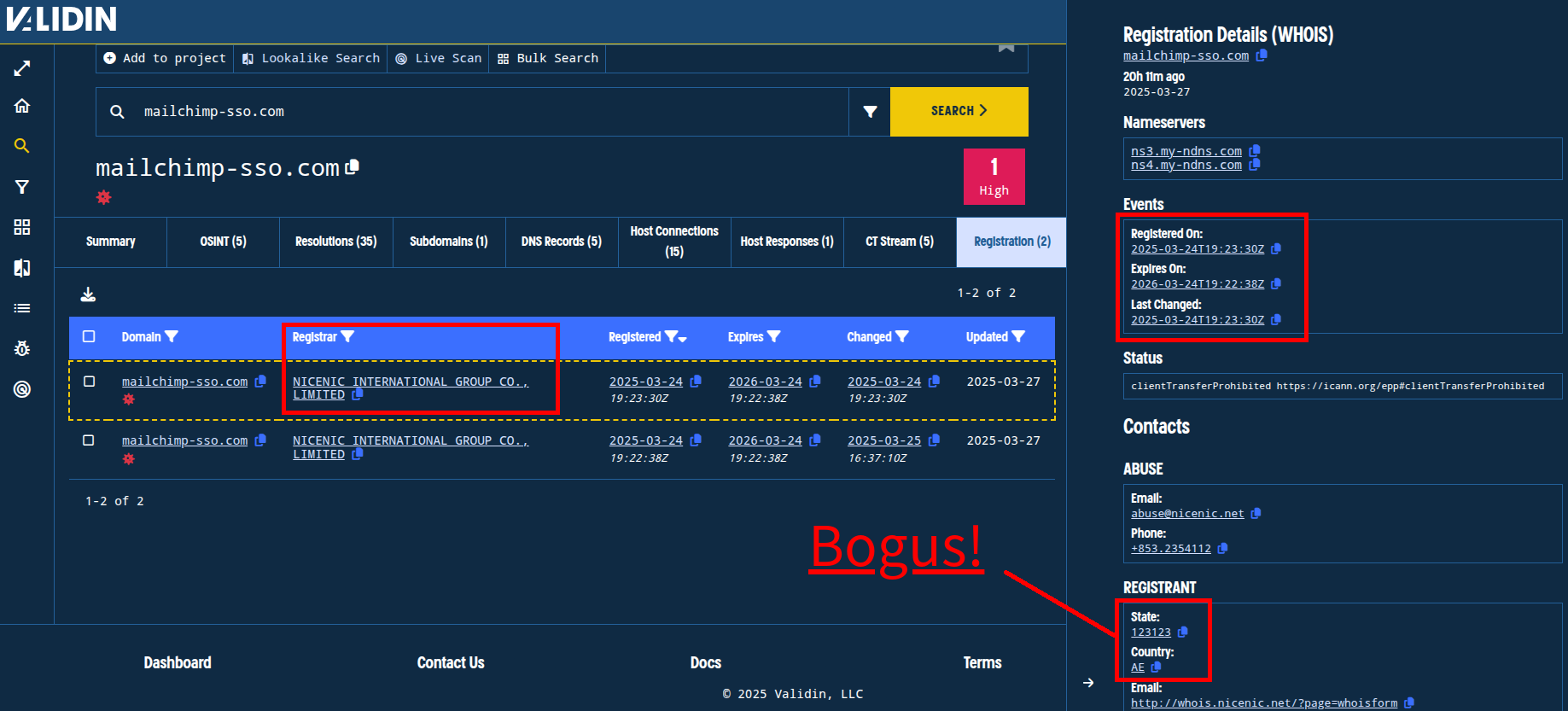
Figure. Bogus value provided for the “State” details in the registration. Note: there are two registration lines in Validin for this domain - one from the registrar and one from the registry.
We will pivot on both of these fields to see if we can find more related domains.
Pivoting Plan
We’ll use a project that we call “Mailchimp Phishing” to track domains and features that we observe in Validin so that we can know when we’re finding overlap with infrastructure and features we’ve already identified.
Having reviewed the initial details about the domain, we’ll consider the following pivots:
- DNS pivots on the IP address
159.100.6[.]244 - Host connection pivots on the banner hash, favicon hash, title, and body hash
- Registration pivots on the registrant state, registrant country, and registration time
Let’s dive in!
DNS Pivots
Pivoting on 159.100.6[.]244, we observe that there are very few connections - only 16 in Validin’s ~6 years of history, with the only the most recent 3 overlapping with the original domain, mailchimp-sso[.]com. We’ll add these other two domains to our project to follow up on later.
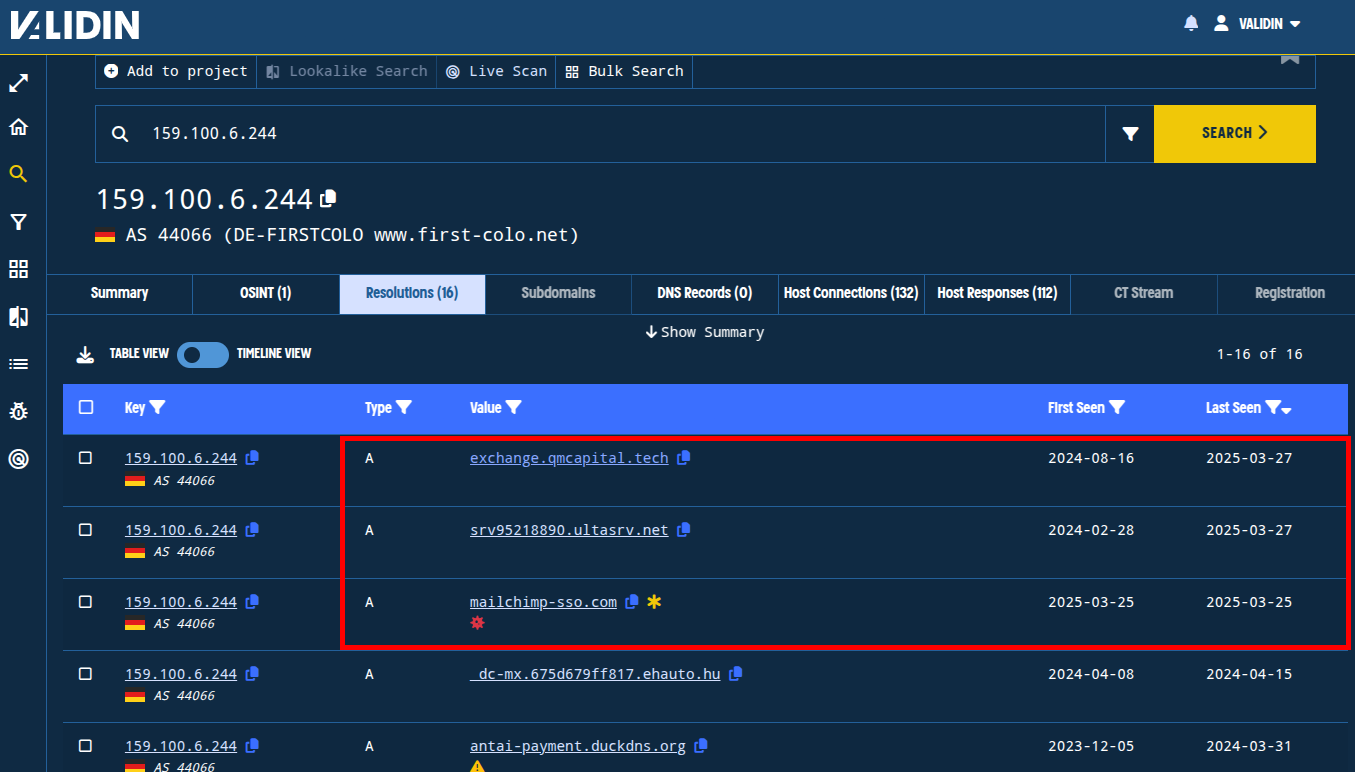
Figure. Finding domains with overlapping DNS history in Validin.
Looking at the host response history for this IP, we note that prior to March 21, the only open port in recent history was 3389, a popular port for the remote desktop protocol, RDP. After that, ports 80, 5000, and 22 were open for at least a few days, and that port 80 appears to have hosted a React application. We see the host response that we’ve already observed on the top line.
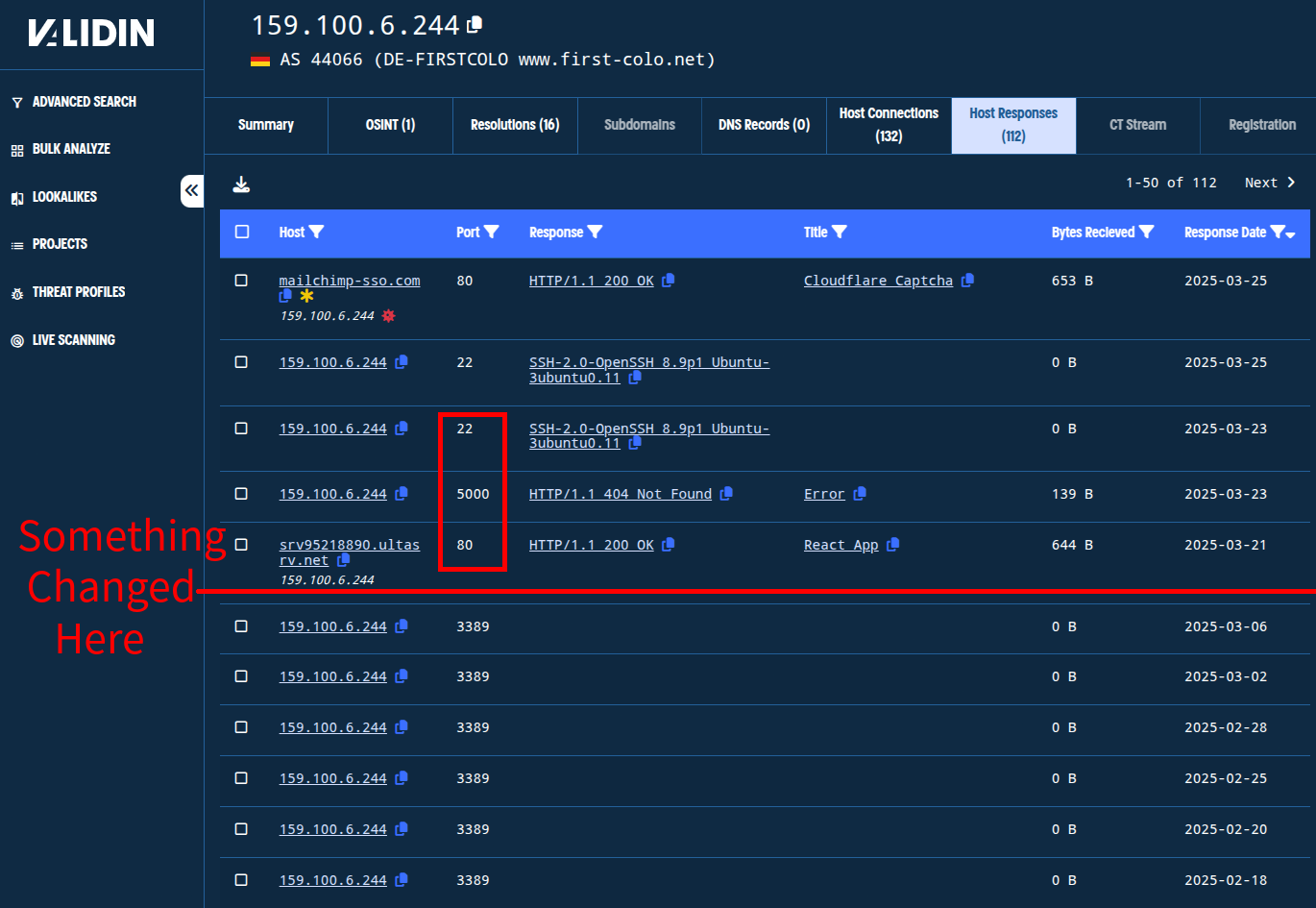
Figure. Observing changes in open ports from Validin’s host response history.
Host Response Pivots
Pivoting on the Banner hash yielded only the original request, meaning that it is too specific to identify other related infrastructure. So, we’ll focus on the favicon hash pivot (2df5eb19ccad19134585f8d52e98ee40) and the title tag pivot (“Cloudflare Captcha”).
The favicon pivot immediately looks interesting. We find only 5 total connections: the two we already knew (the original domain and IP), a Cloudflare proxy IP, and two new domains: mailchimp-ssologin[.]com and server9-mailgun[.]com, which were served by the Cloudflare IP address. We’ll add these domains and the favicon hash to our project.
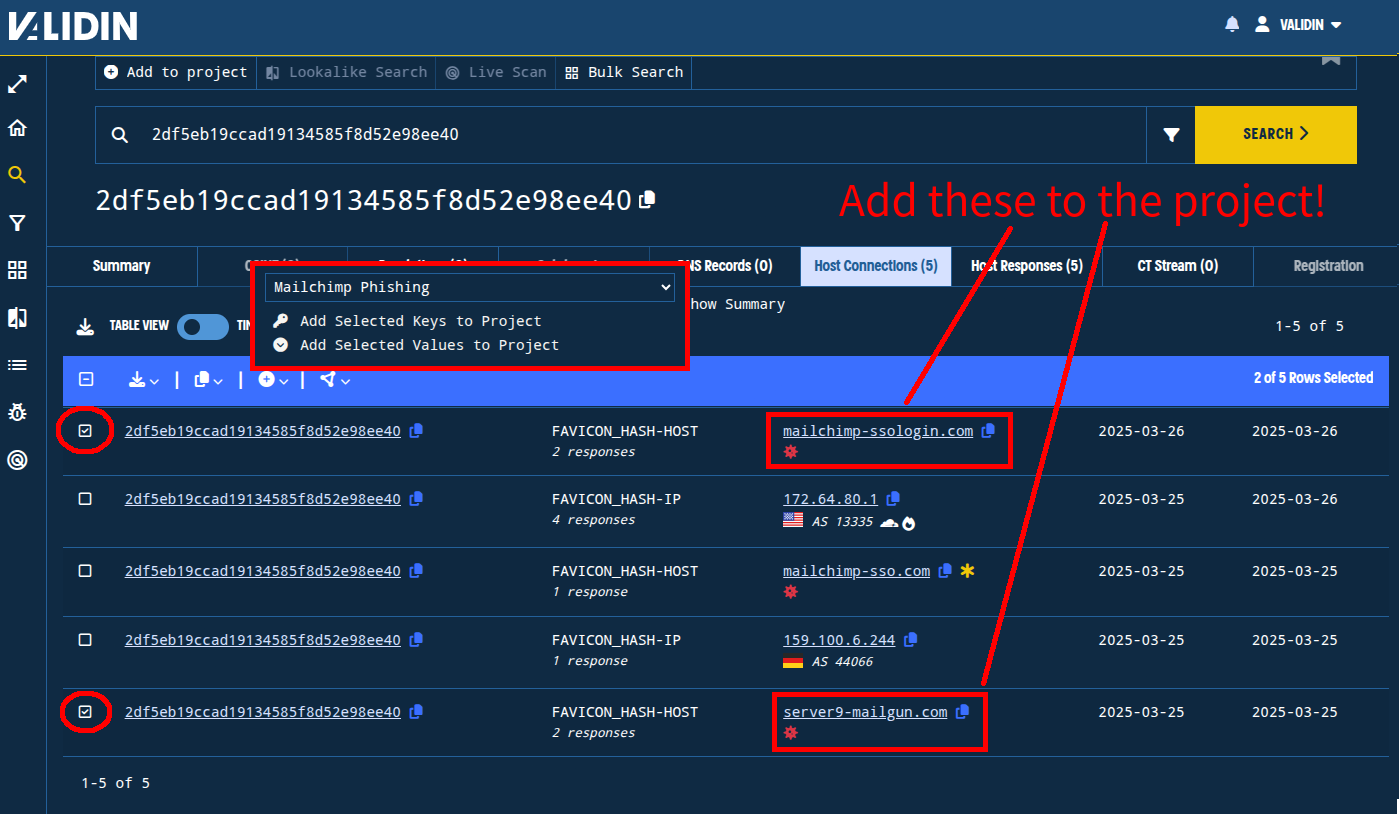
Figure. Identifying and adding newly-discovered connections to our “Mailchimp Phishing” project.
When we look at the connections to the “Cloudflare Captcha” title tag, the results are even more interesting. We find 43 domains and IP addresses with this title tag dating back to mid-2024. For the purposes of this investigation, we’ll focus just on the connections observed in March, which brings the total to 30.
The candidate domain list includes other domains that appear very likely related to the same campaign, with SSO and mailing list themes, and a few with other themes, possibly banking or crypto related.

Figure. Domains and IPs that returned the “Cloudflare Captcha” title tag over the last few days.
The new mailing list-themed domains include (including the root domain only):
sendgridssoservices[.]com
loginportal-sendgrid[.]net
murrez.duckdns[.]org
server9-sendgrid[.]net
hubservices-crm[.]com
Other crypto and banking themed domains include:
asset-hyperliquid[.]com
liquitidy-pepe[.]com
worldofmobile[.]top
eigenlayer-assets[.]com
falseadvertisinginposts[.]com
swell-assets[.]com
iiiuvium-io[.]com
We also see a few additional non-Cloudflare IPs:
176.65.141[.]197
159.100.20[.]154
31.172.83[.]147
We will add all domains and non-Cloudflare IPs to our project.
We’ll also pivot on the favicon hashes that we haven’t seen before:
b636601725429ecab7622d147f928229da369a25b7d91b6533c4576aa529fe9e
From the favicon hashes above, we find a few more domains that we haven’t seen. Of those, we’ll add the following after checking age, response history, and registration details:
activisionsuport[.]com
rseponse25-sendgrid[.]com
rseponse-manageprod[.]com
www[.]rseponse-manageprod[.]com
www[.]rseponse25-sendgrid[.]com
sso-signon[.]com
sso-account[.]com
qmtysv.easypanel[.]host
We’ll also add these IP addresses:
87.121.79[.]41
87.121.79[.]40
79.133.56[.]42
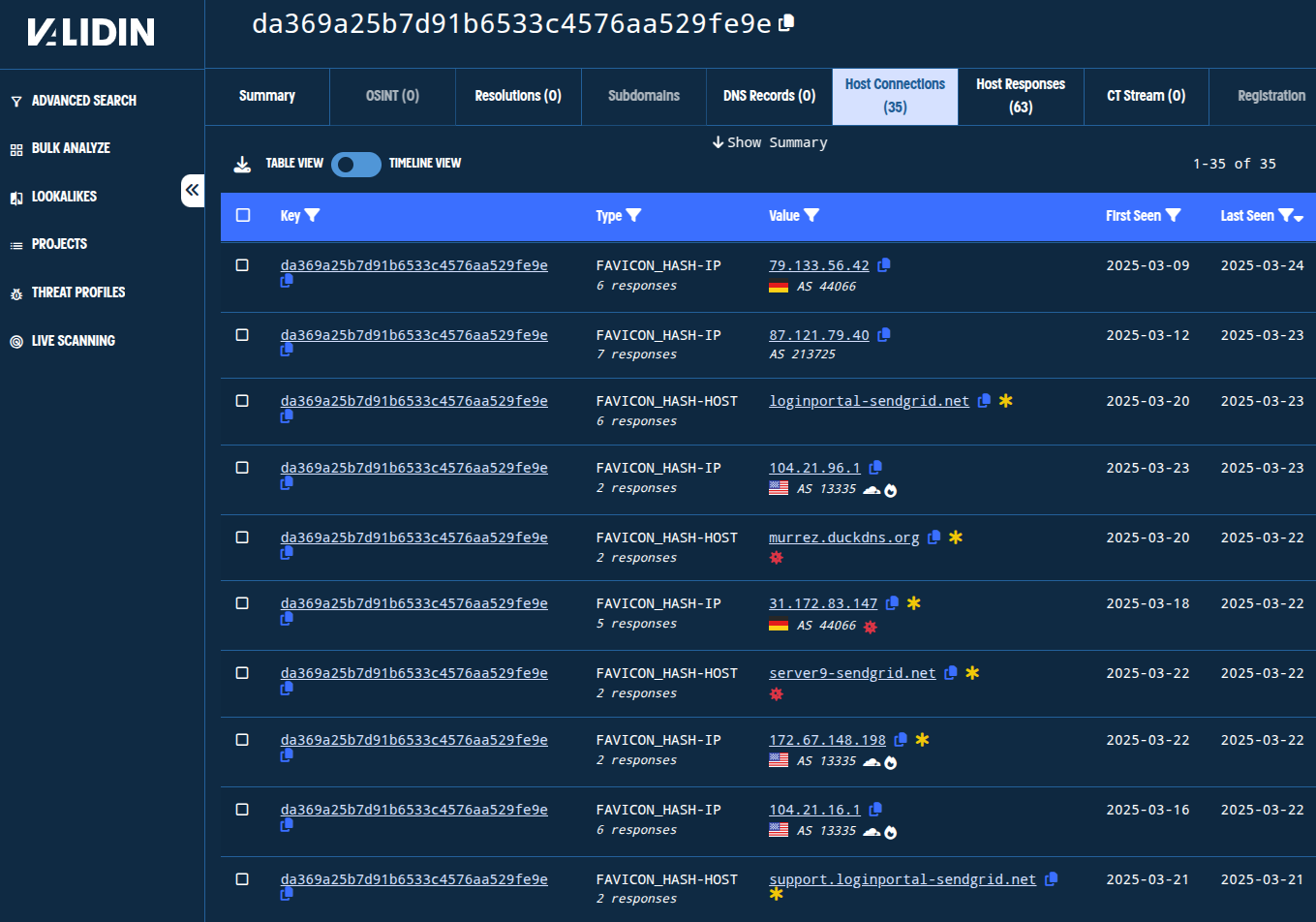
Figure. Host connections from one of the favicon hash pivots.
At this point, we have 38 indicators in our project: 1 title tag, 3 favicon hashes, 5 IP addresses, and 29 domain names.
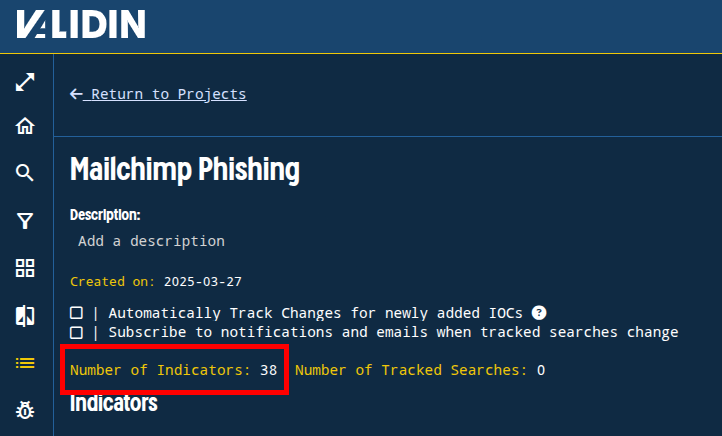
Figure. Quick pivoting on host response and DNS features yielded 37 total new indicators.
Registration Pivots
We learned earlier that the first domain, our ground truth (mailchimp-sso[.]com) , was recently registered on NICENIC and contained bogus registrant details. We’ll pivot on those details and look for other pivots in the domains we gathered from the DNS and host response pivots to see if we can identify additional candidates.
We’ll pivot off of the bogus “State” value of “123123” to see what we can find.
Unsurprisingly, we don’t see a huge number of results, but there are still over 1485 total entries. However, we can see from the first few that we’re likely onto something. So, we’ll filter by the Registrar and filter out anything registered before January 2025 to focus the search.
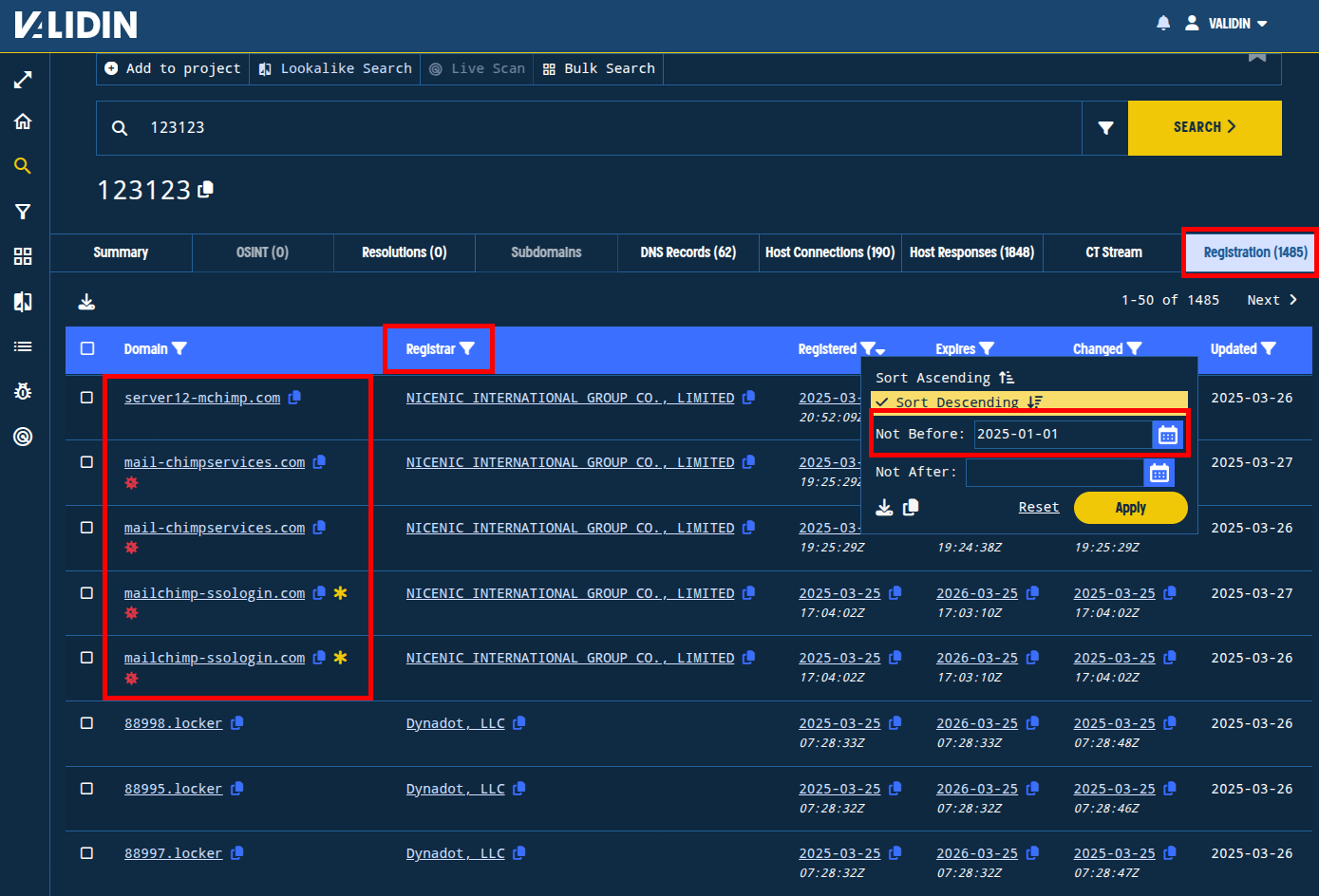
Figure. Observing domains with connections to “123123” and applying Registrar and “Registered Date” filters to focus the results.
From this set, we find a handful of domains already on our list, and a few more that we haven’t seen before, all registered within the last week:
server12-mchimp[.]com
mail-chimpservices[.]com
server9-hubspot[.]com
Repeating this process with registration details from the other domains we’ve collected, we find a number of other features that we can pivot on. A few of these features are highlighted below.
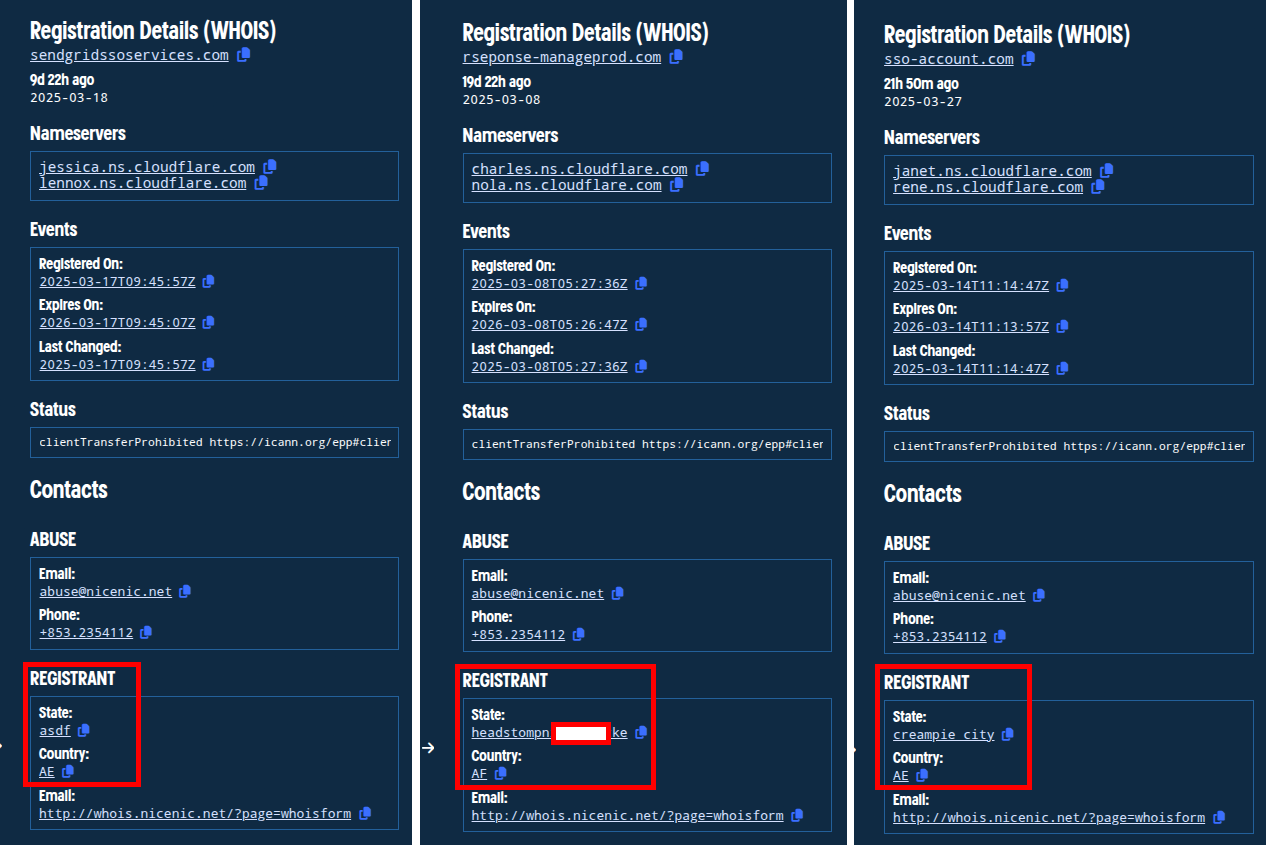
Figure. Pivotable registration features as seen in Validin Enterprise.
Side note
The vast majority of the domains discovered through pivoting were found to use NICENIC as the registrar. However, from the list of domain names discovered through HTTP feature pivoting, the following domain names use different registrars. This does not necessarily mean that these are not connected, as Scattered Spider has been known to use multiple registrars, but it does increase the need for additional validation of the indicators.
Note that unlike the domains above, these domains were registered on Tucows:
iiiuvium-io[.]comswell-assets[.]comeigenlayer-assets[.]comliquitidy-pepe[.com]asset-hyperliquid[.]com
These domains were registered on Web Commerce Communications:
falseadvertisinginposts[.]comactivisionsuport[.]com
This domain was registered on NameSilo:
worldofmobile[.]top
Despite using registrars other than NICENIC, we believe these are related to the original campaign given their age, naming themes, and the fact that they use very specifically-configured host responses.
Connections to Scattered Spider
Troy Hunt described the phishing email he received as creating “just the right amount of urgency without being over the top.” Further the fake login page didn’t arouse suspicion until the damage was done and the credential harvesting and actions that followed were sophisticated and automated. The fake login page used both credentials and an OTP to create an API key in Mailchip then used that new API key to export the mailing list, and this all happened in under a minute.
Troy Hunt’s description of the TTPs leveraged by this attack strongly overlaps with those described by existing research, and the domain names linked to this campaign strongly resemble previous domains linked to Scattered Spider. Further, as described by Wiz last November, Scattered Spider has been known to re-use previously-used domains like mailgun-okta[.]com. The domain mailchimp-sso[.]com, used against Troy Hunt, was previously used by Scattered Spider in 2022 as reported by GroupIB.
Given these similarities, we believe the phishing attempt of Troy Hunt is very likely Scattered Spider.
Further, there are concrete connections between the domains we uncovered in this investigation and other prolific phishing efforts involving Crypto-themed phishing lures (as documented by RacWatchin8872, banthisguy9349, Cipher0091, and many others), and even lost iphone-themed domains associated with smishing campaigns. We cannot definitely say that these are all part of the same threat actor, but there are many similarities, and ultimately, Validin can be leveraged to proactively discover and track these campaigns.
Conclusion
This investigation demonstrates the power of Validin’s DNS history, host response, and WHOIS feature databases for uncovering adversary infrastructure through a unified search interface. By leveraging the Validin platform and the pivoting techniques outlined in this post, threat hunters can efficiently identify related domain names, IP addresses, and patterns, ultimately strengthening their threat intelligence and building confidence in existing findings. The features derived from Validin’s observations enable proactive indicator identification and significantly reduce the time and effort required for in-depth analysis.
Ready to elevate your threat hunting, threat attribution, and incident response efforts? Whether you’re an individual analyst or part of a larger enterprise team, Validin offers solutions that meet your needs. Individual users can create a free account and self-upgrade to access more advanced features and data.
Part of a team? Contact us today to explore our enterprise options and discover how Validin can provide your teams with powerful tools unparalleled data. Let Validin help you work smarter, faster, and more effectively in the fight against cyber threats.
Indicators
mydocconnect[.]me
ichimoco[.]online
murrez.duckdns[.]org
qmcapital[.]tech
928212[.]com
firmware-server12[.]com
456730-cb[.]com
24495-cb[.]com
xn--secure-conbase-8lb[.]com
response20-sendgrid[.]com
response11-sendgrid[.]com
response12-sendgrid[.]com
response13-sendgrid[.]com
response14-sendgrid[.]com
response15-sendgrid[.]com
rseponse25-sendgrid[.]com
response16-sendgrid[.]com
hub-sendgrid[.]com
cloudflare-sendgrid[.]com
complete-sendgrid[.]com
panel-sendgrid[.]com
responsesendgrid[.]com
asset-hyperliquid[.]com
stupid-backend[.]com
recovery-backend[.]com
mysrver-chbackend[.]com
rseponse-manageprod[.]com
74511-icloud[.]com
route-icloud[.]com
help-icloud[.]com
access-icloud[.]com
activity-icloud[.]com
13597-binance[.]com
185679-binance[.]com
mywallet-cbupgrade[.]com
smart-walletupgrade[.]com
cb-smartupgrade[.]com
993248-google[.]com
activity-google[.]com
activity-apple[.]com
liquitidy-pepe[.]com
gmailcare[.]com
mysite-clflre[.]com
90210-coinbase[.]com
19920-coinbase[.]com
456730-coinbase[.]com
114880-coinbase[.]com
74511-coinbase[.]com
715821-coinbase[.]com
187351-coinbase[.]com
591861-coinbase[.]com
849381-coinbase[.]com
2567891-coinbase[.]com
connect1-coinbase[.]com
123902-coinbase[.]com
938822-coinbase[.]com
534432-coinbase[.]com
98732-coinbase[.]com
430932-coinbase[.]com
739472-coinbase[.]com
73872-coinbase[.]com
208972-coinbase[.]com
10382-coinbase[.]com
902392-coinbase[.]com
98392-coinbase[.]com
932892-coinbase[.]com
54892-coinbase[.]com
45623-coinbase[.]com
19723-coinbase[.]com
743823-coinbase[.]com
114823-coinbase[.]com
894833-coinbase[.]com
175643-coinbase[.]com
439843-coinbase[.]com
59843-coinbase[.]com
849383-coinbase[.]com
72883-coinbase[.]com
12983-coinbase[.]com
832983-coinbase[.]com
43983-coinbase[.]com
28983-coinbase[.]com
943993-coinbase[.]com
233904-coinbase[.]com
129934-coinbase[.]com
5897654-coinbase[.]com
789564-coinbase[.]com
734684-coinbase[.]com
293094-coinbase[.]com
24495-coinbase[.]com
connect5-coinbase[.]com
129756-coinbase[.]com
657986-coinbase[.]com
152907-coinbase[.]com
823737-coinbase[.]com
904567-coinbase[.]com
193597-coinbase[.]com
8638-coinbase[.]com
477658-coinbase[.]com
577658-coinbase[.]com
78298-coinbase[.]com
178609-coinbase[.]com
38809-coinbase[.]com
998219-coinbase[.]com
998329-coinbase[.]com
cancel-coinbase[.]com
atlas-coinbase[.]com
819746t-coinbase[.]com
swallet-coinbase[.]com
client-coinbase[.]com
revert-coinbase[.]com
walletwhitelist-coinbase[.]com
trust-coinbase[.]com
activity-coinbase[.]com
firmware-llive[.]com
response-crmsg[.]com
974832-gemini[.]com
185679-gemini[.]com
restore-gemini[.]com
ella-api[.]com
revokecblink[.]com
response-loginportal[.]com
32510-gmail[.]com
7459821-gmail[.]com
193141-gmail[.]com
534212-gmail[.]com
554672-gmail[.]com
7654783-gmail[.]com
185674-gmail[.]com
activity-gmail[.]com
pos-uhaul[.]com
hubservices-crm[.]com
restore-kraken[.]com
help-kraken[.]com
activity-kraken[.]com
mailchimp-ssologin[.]com
secure-kucoin[.]com
sso-signon[.]com
server9-mailgun[.]com
active-mailgun[.]com
support-zoho[.]com
iiiuvium-io[.]com
usw3-twilio[.]com
suite-demo[.]com
live-sso[.]com
mailchimp-sso[.]com
redirect-sso[.]com
server12-mchimp[.]com
inquiry-loginp[.]com
sso-walletmanager[.]com
129756-ledger[.]com
portal-ledger[.]com
revert-ledger[.]com
sso-loginservices[.]com
sendgridssoservices[.]com
mail-chimpservices[.]com
businessqualityins[.]com
review-termsconditions[.]com
responseinquiry-tos[.]com
google-tickets[.]com
coinbase-tickets[.]com
swell-assets[.]com
eigenlayer-assets[.]com
falseadvertisinginposts[.]com
restore-exodus[.]com
ellaredirect[.]com
coinbaseticket[.]com
smartcb-wallet[.]com
cancel-cbwallet[.]com
web-smartwallet[.]com
retired-smartwallet[.]com
update-smartwallet[.]com
panel-smartwallet[.]com
main-smartwallet[.]com
conversion-smartwallet[.]com
recover-smartwallet[.]com
legacy-smartwallet[.]com
sso-account[.]com
myaccount-hbspot[.]com
usw2-hubspot[.]com
server9-hubspot[.]com
activisionsuport[.]com
myw-cbw[.]com
sendgrid-review[.]com
mywallet-cbsmw[.]com
mywallet-cbsmartw[.]com
rseponsequery[.]com
vlasnika[.]info
unlink-trezor[.]io
recovery-trezor[.]io
safetronwallet[.]pro
worldofmobile[.]top
verification-binance[.]us
server9-sendgrid[.]net
loginportal-sendgrid[.]net
qmtysv.easypanel[.]host
stupidredirect[.]xyz
NOTE: the following two domains were inadvertently included in the original post and are NOT malicious:
ultasrv <dot> net
melbourneunirugby <dot> com <dot> au
176.65.141[.]197
159.100.20[.]154
159.100.6[.]244
31.172.83[.]147
b636601725429ecab7622d147f928229
da369a25b7d91b6533c4576aa529fe9e
2df5eb19ccad19134585f8d52e98ee40
2e6d9111c47a892b0bb4bae635cafabd
